AWS Security Hub Automated Remediation Response
Managing enterprise security is costly, high priority and hard! Ignore it at your peril.
We’ve all seen the news reporting the impact of security incidents recently. Reputational damage, shareholder impact, media coverage and not to mention the lack of sleep and effort to remediate. Then how to manage it all again going forward?
AWS Security Hub Automated Remediation Response (SHARR) solution comes in-built as part of our AWS Foundations (AWSF) implementation which provides you with some well-earned peace of mind by enabling real-time detection, alerting and automated-remediation of security threats before the media start queuing at the gates. Not only does the security management process become more efficient, it will also reduce the security team’s workload. Nice to be able to get some time back to be able to focus on more proactive tasks.
In this post, we cover detailed information on SHARR technical design, architecture and implementation. We have also provided a recorded video session which demonstrates it’s core functionality.
Design Overview
AWSF Security Hub Automated Remediation Response (SHARR) implementation closely resembles the solution found in AWS solutions library with minor differences and customisations. All components in this solution design uses AWS native services and no third party applications, tools and/or services are included. Thus, not only does it prove to be an efficient and cost-effective solution, it also provides assurance from a warranty perspective since on-going support for all services are managed by AWS.
SHARR solution utilises prepackaged security standards that are available for AWS Security Hub, such as the CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark, AWS Foundational Security Best Practices, and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). These help evaluate the security posture of all AWS accounts and resources against well known industry security standards.
Key Components
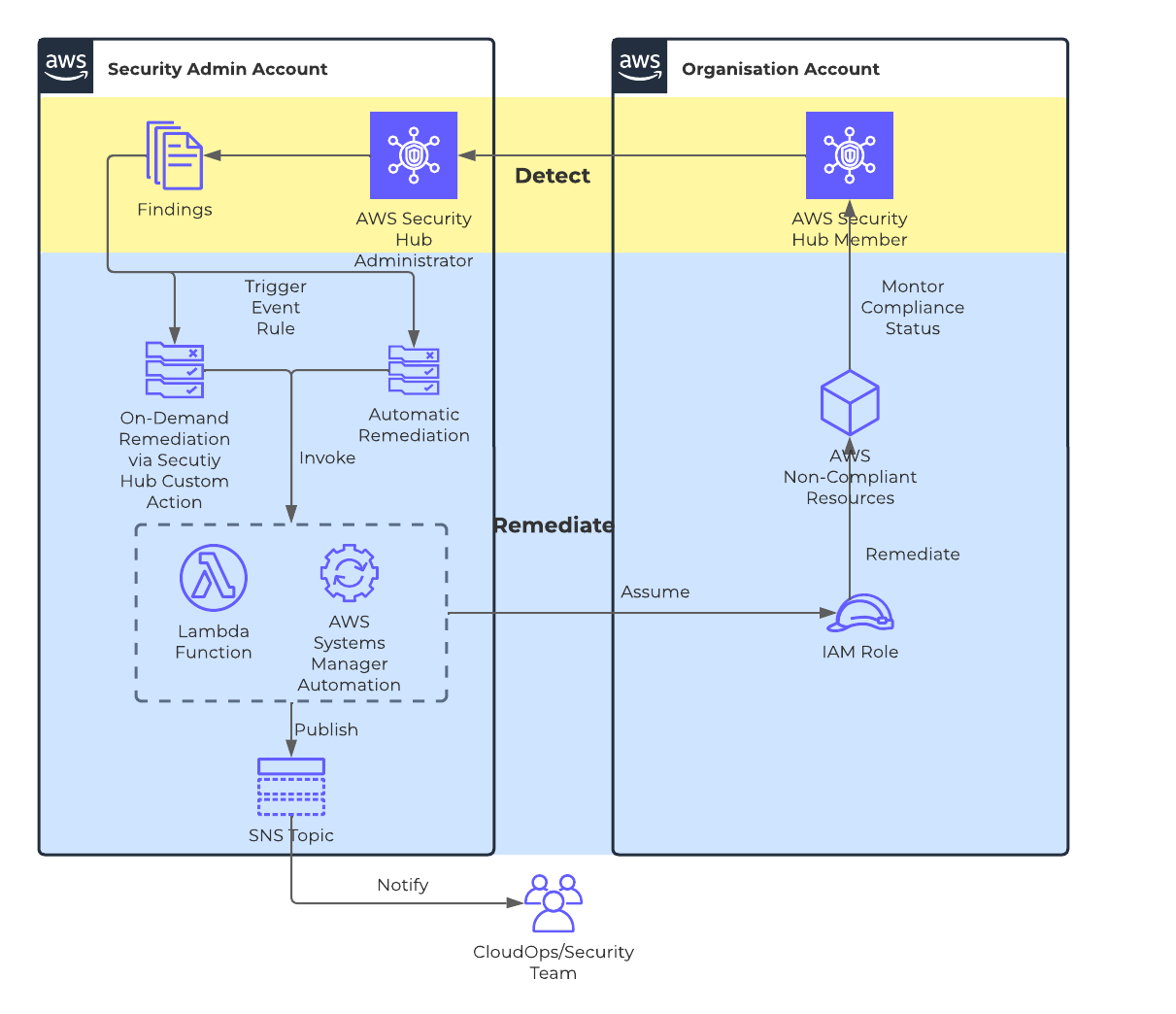
- AWS Security Hub is enabled (per AWS region) in every AWS account within an AWS Organization with a dedicated delegated administrator account. This ensures Security Hub findings from all AWS accounts are consolidated in delegated administrator account.
- Two CloudWatch event rules are configured per security hub control ID in delegated security administrator AWS account. One rule is automatically triggered when a non-compliant security hub finding is detected from a given AWS account while the other rule can be triggered on-demand via invocation of security hub custom actions.
- These event rules invoke AWS Lambda functions which are also provisioned in the delegated security administrator AWS account. The remediation logic embedded in Lambda functions uses IAM role(s) in target AWS account(s) to assume and remediate corresponding AWS resource(s).
- Finally a notification is sent via SNS Topic to the end-user that describes the remediation status.
Setup
AWS Security Hub
AWS Security Hub service needs to be enabled and configured across relevant AWS accounts prior to implementing SHARR solution. The following steps outlines the process of setting up AWS Security Hub in a multi account AWS environment with a designated security administrator account.
- Enable AWS Security Hub service in all accounts and all regions within an AWS organization. This is because AWS Security Hub is a regional service and we want to ensure all regions are covered as part of the security assessment/posture.
- In each AWS region, designate a dedicated security account as the delegated administrator for AWS Security Hub service.
- In each AWS region, enable member accounts from the delegated administrator account. Member accounts can be automatically enabled if required or invited if they are external and not part of the AWS organization.
- Enable Security Hub cross-region aggregation in your home AWS region of delegated administrator account. This will aggregate findings from all other regions to the specified home region. Please note some regions are excluded or not supported for aggregation. In that case, choose another region as the aggregated region.
- Finally, disable Security Hub controls depending on overall enterprise architecture.
AWS Security Hub Automated Remediation Response (SHARR)
All SHARR components are provisioned and configured in the aggregated region of delegated security administrator account. Our solution includes remediations for a list of Security Hub controls (this list will grow overtime as more and more features are added) which has too much content to cover over a single blog post. Therefore, steps mentioned below elaborates on remediation for Security Hub control ID EC2.2 only (the same logic can then be applied to remediate other Security Hub controls).
- Create KMS key to encrypt SHARR data at rest and in-transit (an example CloudFormation template is given below).
---
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: Setup Security Hub Automated Remediation Response KMS Key.
Resources:
KmsKey:
Type: AWS::KMS::Key
Properties:
Enabled: true
EnableKeyRotation: true
KeyPolicy:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Id: kms-sharr
Statement:
- Sid: Enable IAM User Permissions
Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS: !Sub arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:root
Action: kms:*
Resource: '*'
- Sid: Allow Lambda access to key
Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- kms:Decrypt
- kms:GenerateDataKey*
Resource: '*'
KmsKeyAlias:
Type: AWS::KMS::Alias
Properties:
AliasName: alias/sharr
TargetKeyId: !Ref KmsKey
- Create SNS topic to send SHARR notifications (an example CloudFormation template is given below).
---
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: Setup Security Hub Automated Remediation Response SNS Topic.
Parameters:
KmsKeyArn:
Type: String
Description: ARN of KMS key created in step 1.
NotifyEmailAddress:
Type: String
Description: Email address to send SHARR notifications.
SnsTopicName:
Type: String
Description: Name of SNS topic to publish SHARRR notifications.
Resources:
SnsTopic:
Type: AWS::SNS::Topic
Properties:
TopicName: !Ref SnsTopicName
KmsMasterKeyId: !Ref KmsKeyArn
Subscription:
- Endpoint: !Ref NotifyEmailAddress
Protocol: email
SnsTopicPolicy:
Type: AWS::SNS::TopicPolicy
Properties:
Topics:
- !Ref SnsTopic
PolicyDocument:
Statement:
- Sid: allowAWSLambdaToPublish
Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sns:Publish
Resource:
- !Ref SnsTopic
Condition:
StringEquals:
aws:SourceAccount: !Ref AWS::AccountId
- Create Lambda function which will be invoked via CloudWatch event rules (created in step 5) to perform remediation of non-compliant resource(s) for EC2.2 security control in corresponding AWS account(s) (an example CloudFormation template is given below). Contents of Lambda function codebase and it’s supported libraries will be briefly covered in the demo session. We recommend browsing through AWS solutions implementation to use as an example or starting point.
---
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: Setup Security Hub Automated Remediation Response Lambda Function.
Parameters:
CwLogGroupName:
Type: String
Description: Name of CloudWatch log group name which will be used to store Lambda function logs.
CwLogGroupRetentionInDays:
Type: Number
Description: Number of days to retain Lambda CloudWatch logs.
KmsKeyArn:
Type: String
Description: ARN of KMS key created in step 1.
LambdaFuncName:
Type: String
Description: Name of Lambda function.
LambdaFuncHandler:
Type: String
Description: Name of Lambda function handler.
LambdaRoleName:
Type: String
Description: Name of IAM role used for Lambda function.
LambdaRolePath:
Type: String
Description: Path of IAM role used for Lambda function.
RemediateRoleName:
Type: String
Description: Name of IAM role provisioned in target AWS accounts (created in step 6) which will be assumed to remediate EC2.2 control.
RemediateRolePath:
Type: String
Description: Path of IAM role provisioned in target AWS accounts (created in step 6) which will be assumed to remediate EC2.2 control.
S3BucketName:
Type: String
Description: Name of S3 bucket where lambda archive is located.
S3Key:
Type: String
Description: S3 key of lambda archive.
SnsTopicArn:
Type: String
Description: ARN of SNS topic (created in step 2 above) to send SHARR notifications.
Resources:
IamRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Version: '2012-10-17'
ManagedPolicyArns:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AWSLambdaExecute
Path: !Ref LambdaRolePath
RoleName: !Ref LambdaRoleName
Policies:
- PolicyDocument:
Statement:
- Action:
- sns:Publish
Effect: Allow
Resource: !Ref SnsTopicArn
- Action:
- kms:Decrypt
- kms:GenerateDataKey*
Effect: Allow
Resource: !Ref KmsKeyArn
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Resource: !Sub arn:aws:iam::*:role/${RemediateRolePath}${RemediateRoleName}
PolicyName: remediate-ec2-2-control
LogGroup:
Type: AWS::Logs::LogGroup
Properties:
LogGroupName: !Ref CwLogGroupName
RetentionInDays: !Ref CwLogGroupRetentionInDays
LambdaFunction:
DependsOn:
- LogGroup
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
Code:
S3Bucket: !Ref S3BucketName
S3Key: !Ref S3Key
DeadLetterConfig:
TargetArn: !Ref SnsTopicArn
FunctionName: !Ref LambdaFuncName
Handler: !Ref LambdaFuncHandler
Role: !Sub ${IamRole.Arn}
Runtime: python3.8
Timeout: 300
Environment: # You can either hardcode values of relevant target AWS resources in Lambda code itself OR pass them via environment variable as shown below.
Variables:
REMEDIATE_ROLE_PATH: !Ref RemediateRolePath
REMEDIATE_ROLE_NAME: !Ref RemediateRoleName
SNS_TOPIC_ARN: !Ref SnsTopicArn
- Create Security Hub custom action to enable on-demand remediation of resources (an example using AWS CLI is given below). Please take note of the value used for ID because it will be used when creating CloudWatch event rule in step 5.
aws securityhub create-action-target --name "EC2.2" --description "Remediates security control EC2.2" --id "EC22"
- Create two CloudWatch Event Rules to capture events generated via Security Hub findings. One rule will automatically be triggered based on new findings that are non-compliant for EC2.2 control ID are generated. The other rule will be triggered when invoked via Security Hub custom action created in step 1 (an example of CloudFormation template is given below).
---
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: Setup Security Hub Automated Remediation Response CloudWatch Event Rules.
Parameters:
LambdaFuncArn:
Type: String
Description: ARN of Lambda function created in step 3.
SecHubCustomActionId:
Type: String
Description: ID of Security Hub custom action created in step 4.
Resources:
RemediateEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
Description: >
Remediate Security Hub control EC2.2 when invoked via custom action.
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.securityhub
detail-type:
- 'Security Hub Findings - Custom Action'
resources:
- !Sub arn:aws:securityhub:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:action/custom/${SecHubCustomActionId}
Name: sharr-custom-action-ec2-2
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Arn: !Ref LambdaFuncArn
Id: LambdaFunction
AutoRemediateEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
Description: >
Auto remediate Security Hub control EC2.2.
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.securityhub
detail-type:
- 'Security Hub Findings - Imported'
detail:
findings:
Compliance:
SecurityControlId: ['EC2.2']
Workflow:
Status:
- NEW
Name: sharr-ec2-2
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Arn: !Ref LambdaFuncArn
Id: LambdaFunction
RemediateLambdaPermission:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Permission
Properties:
Action: lambda:InvokeFunction
FunctionName: !Ref LambdaFuncArn
Principal: events.amazonaws.com
SourceArn: !Sub ${RemediateEventRule.Arn}
AutoRemediateLambdaPermission:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Permission
Properties:
Action: lambda:InvokeFunction
FunctionName: !Ref LambdaFuncArn
Principal: events.amazonaws.com
SourceArn: !Sub ${AutoRemediateEventRule.Arn}
- Created IAM role in all member AWS accounts which will grant Lambda function (created in step 3) with required permissions to remediate non-compliant resource(s) (an example of CloudFormation template is given below).
---
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: Setup Security Hub Automated Remediation Response IAM Roles.
Parameters:
LambdaRoleName:
Type: String
Description: Name of IAM role used for Lambda function created in step 3.
LambdaRolePath:
Type: String
Description: Path of IAM role used for Lambda function created in step 3.
RemediateRoleName:
Type: String
Description: Name of IAM role which will grant permissions to remediate EC2.2 control.
RemediateRolePath:
Type: String
Description: Path of IAM role which will grant permissions to remediate EC2.2 control.
SecurityHubAdminAccountId:
Type: String
Description: Security Hub administrator account ID
Resources:
RemediateRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS: !Sub arn:aws:iam::${SecurityHubAdminAccountId}:role${LambdaRolePath}${LambdaRoleName}
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Version: '2012-10-17'
ManagedPolicyArns:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AWSLambdaExecute
Path: !Ref RemediateRolePath
RoleName: !Ref RemediateRoleName
Policies:
- PolicyDocument:
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroup*
- ec2:DescribeVpcs
- ec2:DescribeSecurityGroup*
- ec2:RevokeSecurityGroup*
- ec2:UpdateSecurityGroupRuleDescriptions*
- ec2:CreateTags
Resource: '*'
PolicyName: sharr-ec2-2
Demo
The most common attack vector for hackers to gain access to systems/data hosted within AWS is via exploiting mis-configured S3 buckets and/or un-restricted VPC security group rules. Therefore, our live demo focuses on how to pro-actively and efficiently remediate these AWS resources in a multi account AWS environment.
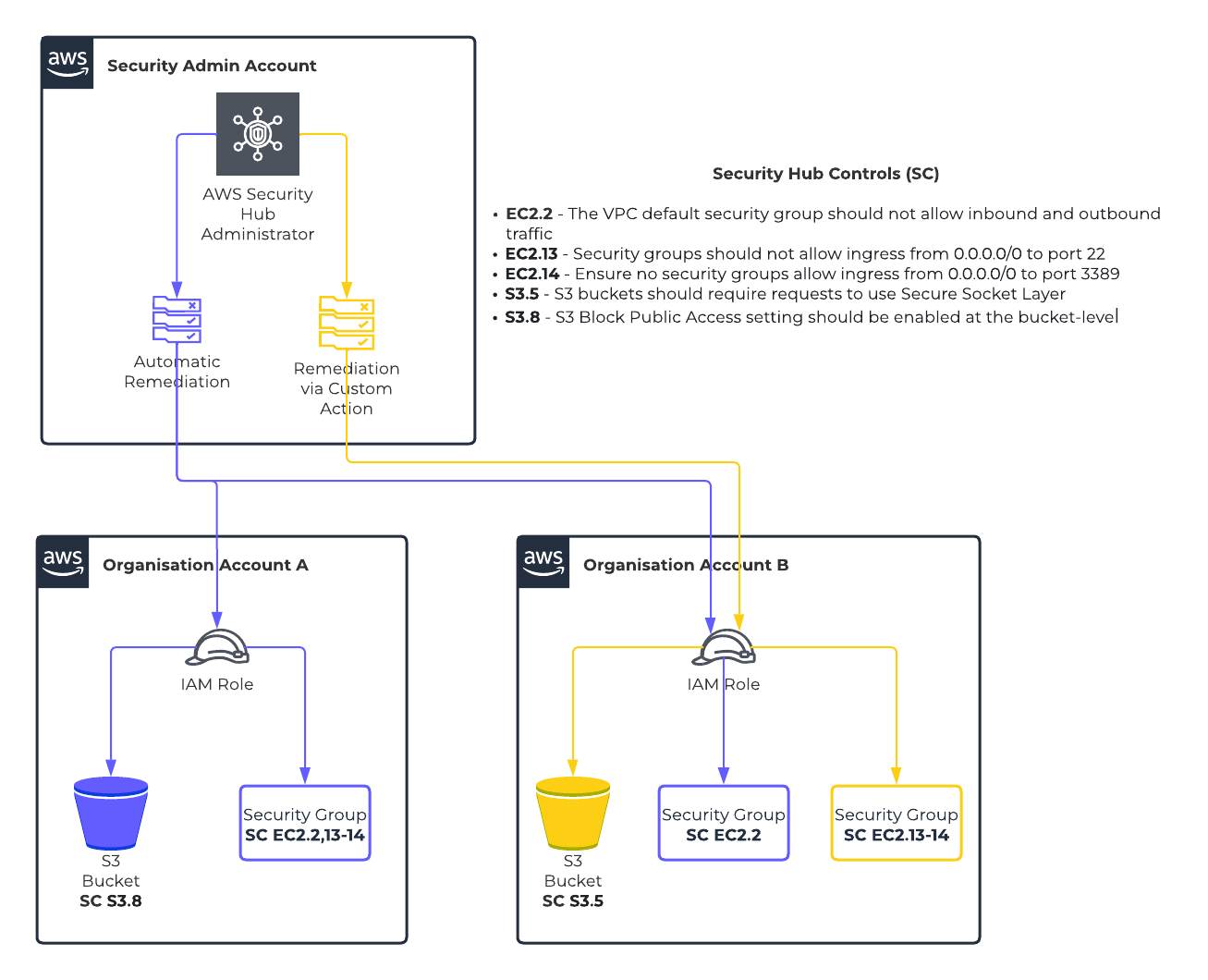
The scenario given above has the following configurations:
- There is a designated security account configured as the Security Hub administrator.
- AWS resources will be created in two member accounts A & B to showcase automated & on-demand remediations.
- Automated remediation of AWS resources within member accounts is based per security control.
- EC2.2 – Both accounts A and B are configured for automatic remediation.
- EC2.13-14 – Only account A is automatically remediated while account B can be remediated via Security Hub custom action invocation,
- S3.5 – Both accounts A and B can only be remediated via custom action invocation.
- S3.8 – Both accounts A and B are configured for automatic remediation.